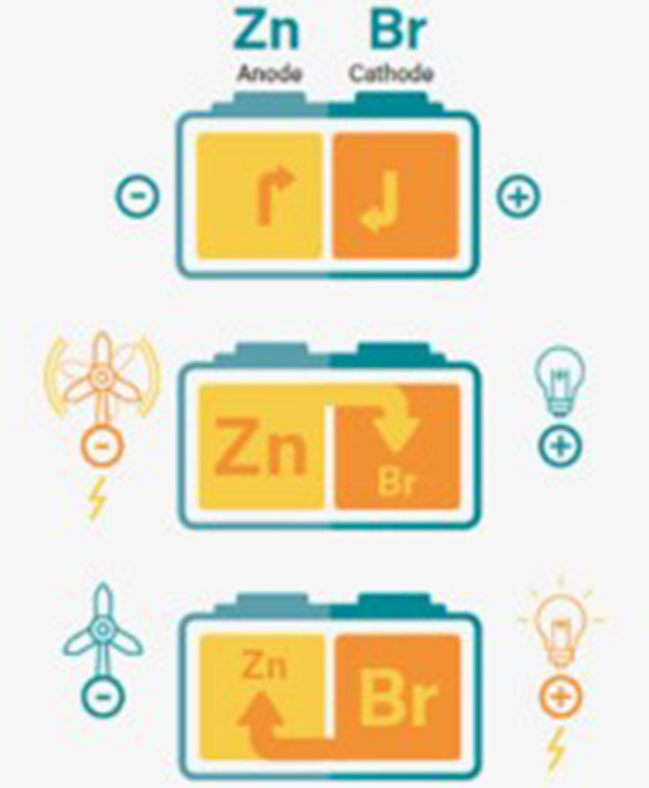
In conventional secondary (rechargeable) batteries, energy is charged and discharged in the active masses of the electrodes. A flow battery is also a rechargeable battery, but the energy is stored in one or more electro active species which are dissolved in liquid electrolytes.
The electrolytes are stored externally in tanks and pumped through the electrochemical cell that converts chemical energy directly to electricity and vice versa. The power is defined by the size and design of the electrochemical cell whereas the energy depends on the size of the tanks.
A flow battery offers the inherent safety of storing the active materials separately from the reactive point source. Other advantages are quick response times, high electricity-to-electricity conversion efficiency, simple state-of-charge indication based on electro-active concentrations, low maintenance, tolerance to overcharge and over discharge, and the ability for deep discharges without affecting cycle life.
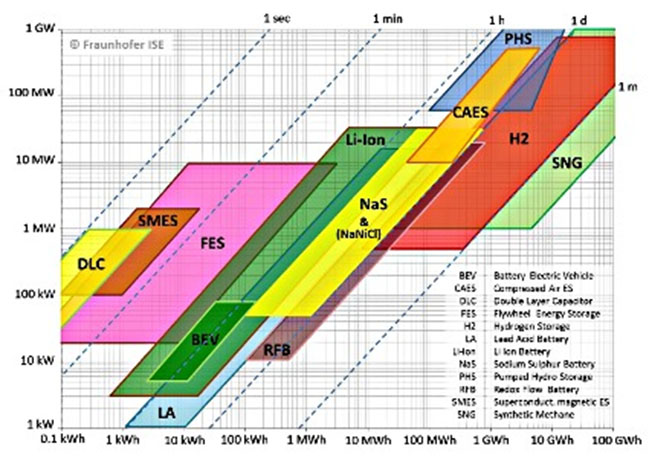
With this characteristic flow batteries can be fitted to a wide range of stationary applications.